- Your cart is empty
- Continue Shopping
Pipetting Techniques 101: Tips for Accurate and Reliable Lab Results
- Pipette
- Posted on
-
by perf__products
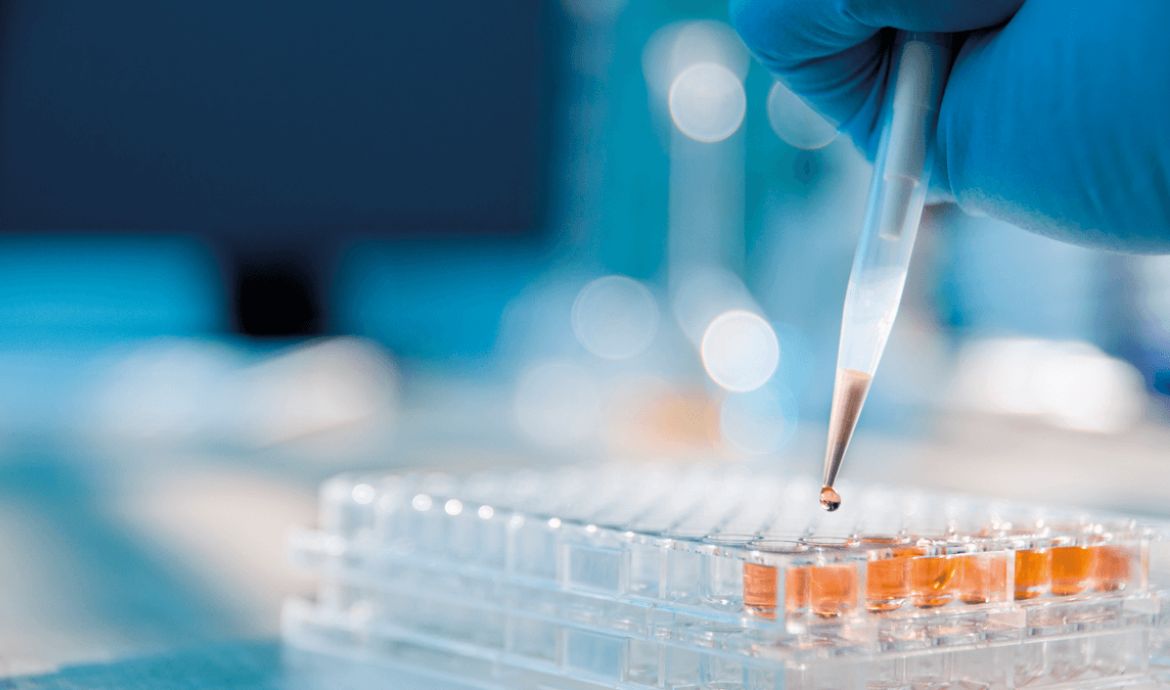
Pipetting is one of the most routine yet essential tasks in any laboratory, and mastering the right techniques is key to achieving accurate, consistent, and reliable results. Poor pipetting practices can lead to measurement errors, contamination, and compromised experimental outcomes. Whether you’re a seasoned lab professional or new to pipetting, this guide covers fundamental tips and techniques to help you get the best results.
1. Choose the Right Pipette and Tips for Your Application
Selecting the correct pipette type and tips is the first step toward accuracy:
- Volume Matching: Use a pipette that has a volume range close to the desired volume. Avoid using a large pipette to measure very small amounts, as this can reduce accuracy.
- Tip Quality: High-quality, compatible tips ensure a proper seal and accurate liquid transfer. Avoid reusing tips to prevent cross-contamination.
- Compatibility: Check that the tips are compatible with your pipette brand to ensure a secure fit.
2. Pre-Wet the Pipette Tip
Pre-wetting the pipette tip helps to condition it, which minimizes volume loss due to evaporation or surface retention:
- Aspirate and dispense the liquid once or twice before the actual transfer.
- This technique is especially important when working with volatile or viscous solutions, as it helps deliver a consistent volume with each transfer.
3. Set the Correct Pipetting Speed
Proper control over the pipetting speed is essential for avoiding air bubbles, splashes, or loss of volume:
- Slow and Steady: Aspirate and dispense slowly to reduce bubbles and ensure a consistent flow.
- Pause After Aspiration: Pausing for a moment after aspiration allows the liquid to fully enter the tip, reducing errors in measurement.
4. Maintain the Correct Pipetting Angle
The angle at which you hold the pipette while aspirating and dispensing affects the precision of your results:
- Upright Position: Hold the pipette vertically when aspirating liquid, particularly for smaller volumes.
- 45-Degree Dispensing: When dispensing, a slight angle (around 45 degrees) helps ensure complete transfer without droplets adhering to the tip.
5. Immerse the Tip Properly
The depth at which the pipette tip is immersed in the liquid plays a crucial role in accuracy:
- Optimal Depth: For small volumes, submerge the tip only 2-3 mm below the surface. For larger volumes, immerse it 5-6 mm.
- Avoid Over-Immersion: Immersing too deeply can lead to excess liquid sticking to the outside of the tip, leading to errors in measurement.
6. Use Consistent Plunger Pressure
Consistent and gentle pressure on the plunger helps ensure that each aspiration and dispense is uniform:
- Use the First Stop: Press the plunger to the first stop for aspiration, then to the second stop for complete dispensing.
- Avoid Jerky Movements: Apply smooth, controlled pressure to reduce variability and prevent air bubbles in the sample.
7. Minimize Residual Drops
Leaving residual drops in the pipette tip can compromise accuracy, especially when working with small volumes:
- Touch-Off Technique: Touch the pipette tip to the side of the receiving container to release any remaining droplets.
- Use Blow-Out Pipettes: Some pipettes are designed with a “blow-out” feature, allowing for complete liquid dispensing. Make sure you use this if your pipette has it.
8. Work at Consistent Temperatures
Temperature differences can significantly impact pipetting accuracy, especially for low volumes or sensitive applications:
- Avoid Hot or Cold Surfaces: Work in a temperature-controlled environment to maintain liquid and pipette temperature consistency.
- Acclimate Pipettes and Samples: Allow liquids, pipettes, and tips to equilibrate to room temperature before use, particularly if they’ve been stored in a refrigerator.
9. Regularly Calibrate and Clean Pipettes
Regular calibration and cleaning ensure that your pipettes maintain their accuracy over time:
- Calibration: Schedule pipette calibration based on usage frequency, especially for critical applications. Many labs recommend calibration every 3-6 months.
- Cleaning: Clean pipettes according to the manufacturer’s instructions to avoid contamination and maintain performance. Pay special attention to the shaft and piston, as dirt and residue can interfere with pipette function.
10. Practice Proper Pipette Storage
Storing pipettes correctly can prevent mechanical damage and ensure they remain calibrated:
- Upright Position: Store pipettes in an upright position on a stand to prevent liquids from entering the pipette body.
- Avoid Exposure to Contaminants: Keep pipettes in a clean, dry environment to avoid dust and chemical exposure, which can impact performance over time.
11. Avoid Common Pipetting Mistakes
Even experienced lab professionals can make pipetting errors. Here are a few common mistakes to watch out for:
- Using the Wrong Volume Setting: Double-check your volume settings before aspirating.
- Not Changing Tips Between Samples: Avoid reusing tips, as this can lead to sample contamination.
- Rapid Pipetting: Avoid rapid plunger movements, which can introduce air bubbles and reduce precision.
12. Final Thoughts
Achieving consistent and reliable results in the lab depends on mastering these pipetting techniques. Taking the time to implement each of these practices will help you reduce errors, improve accuracy, and save valuable time in redoing experiments. By following these tips, lab professionals can confidently rely on their pipetting skills to support successful experiments and achieve accurate, reproducible results.


